Roles¶
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Getting Started
- Role Management Interface
- Standard Roles
- Creating Custom Roles
- Permission System
- Module Permissions
- Operation Permissions
- Assigning Permissions
- Role Hierarchy
- Editing Roles
- Role Assignment
- Permission Inheritance
- Best Practices
- Security Considerations
- Troubleshooting
Overview¶
The Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system enables administrators to define granular permissions for user groups with fine-grained authorization at both the action level and data level. Create custom roles tailored to your organization's workflow, assign specific permissions with data filters, and maintain security through principle of least privilege.
Key Capabilities:
- Pre-configured standard roles for common warehouse positions
- Custom role creation with granular permission control
- Fine-grained permission system: Module-action based authorization (PermissionGuard)
- Data-level access control: Row-level filtering (e.g., customer-scoped data)
- Permission groups organized by functional module
- Role inheritance and permission composition
- Audit trail of role changes
- User-to-role assignment tracking
- Read, create, update, delete (CRUD) permission granularity
- Consistent 403 forbidden responses with NoAccess UI component
Getting Started¶
Prerequisites¶
Before managing roles:
- Administrator Access: System Administrator role required for role management
- Organization Structure: Understanding of job functions and responsibilities
- Security Requirements: Knowledge of compliance and access control needs
- Workflow Analysis: Identification of operational permission requirements
When to Manage Roles¶
Role management is essential for:
- Initial Setup: Configuring roles during system implementation
- Organizational Changes: Creating roles for new positions or departments
- Security Compliance: Implementing least privilege access controls
- Workflow Optimization: Adjusting permissions to match operational needs
- Audit Response: Modifying roles based on security reviews
- Custom Operations: Creating specialized roles for unique workflows
Role Management Interface¶
Access role management through the Administration section:
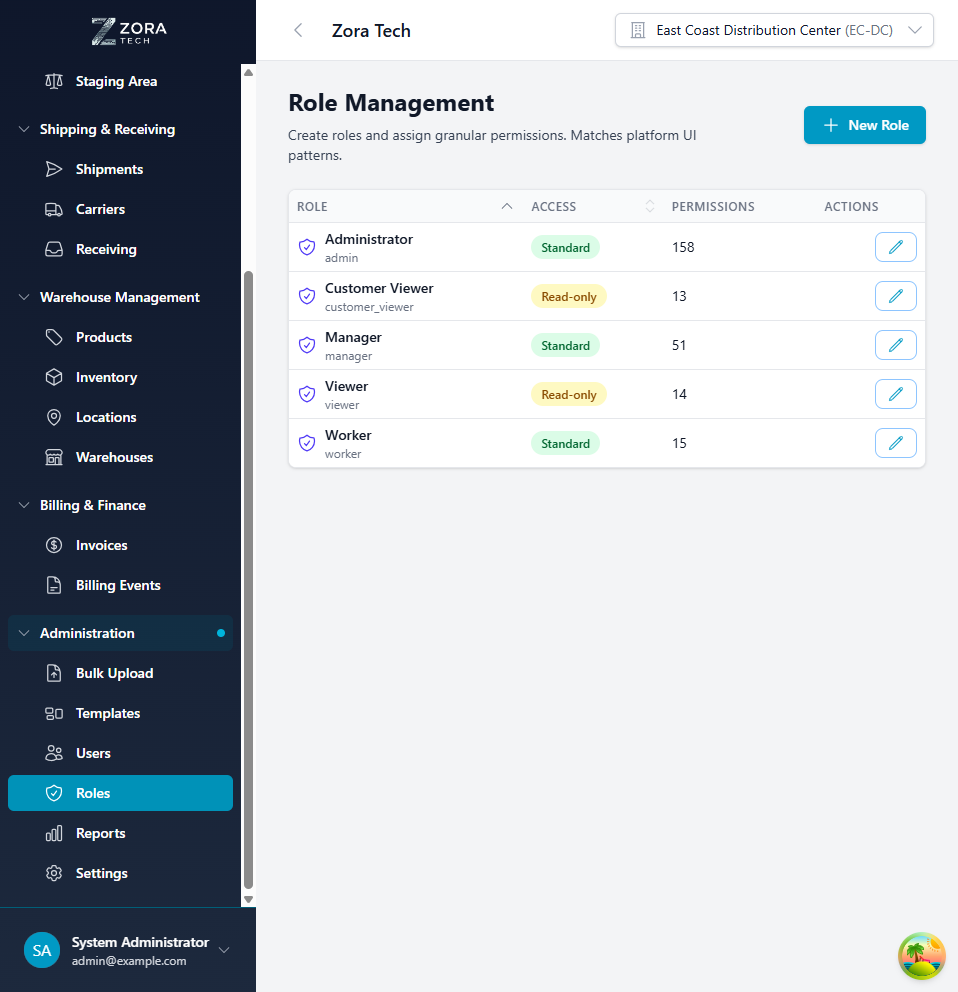
Interface Components:
- Search Bar: Find roles by name or description
- Role Cards: Display each role with key information
- Permission Count: Number of permissions assigned to role
- User Count: Number of users assigned to role
- Action Buttons: Edit, duplicate, or delete roles
- Add Role Button: Create new custom roles
Role Card Information:
- Role Name: Display name of the role
- Description: Brief explanation of role purpose
- Permissions: Total count of assigned permissions
- Users: Number of active users with this role
- System/Custom: Badge indicating built-in or custom role
- Last Modified: Timestamp of last role update
Standard Roles¶
The platform includes pre-configured roles for common warehouse operations:
System Administrator¶
Access Level: Full system access
Permissions: - All modules: Complete CRUD access - User management: Create, edit, delete users - Role management: Create and modify all roles - System configuration: All settings and preferences - Warehouse management: All warehouse operations - Audit logs: View all system activities
Typical Users: - IT administrators - Platform administrators - System integrators
Permission Count: 150+ permissions
Warehouse Manager¶
Access Level: Warehouse-wide operational management
Permissions: - Inventory: Full CRUD access - Orders: Full CRUD access, allocation, fulfillment - Receiving: Full CRUD access, approval workflows - Shipping: Full CRUD access, carrier integration - Locations: Full CRUD access, location management - Reporting: All warehouse reports - Products: View, limited edit (no deletion) - Users: View only (no user management)
Typical Users: - Warehouse managers - Operations managers - Shift supervisors
Permission Count: 85 permissions
Inventory Manager¶
Access Level: Inventory-focused operations
Permissions: - Products: Full CRUD access - Inventory: Full CRUD access, adjustments, transfers - Cycle Counts: Full CRUD access - Locations: Full CRUD access - LPNs: Full CRUD access - Orders: View only - Receiving: View only - Reporting: Inventory-related reports
Typical Users: - Inventory specialists - Stock control managers - Cycle count coordinators
Permission Count: 55 permissions
Receiving Clerk¶
Access Level: Receiving operations
Permissions: - Receiving Orders: Full CRUD access - LPN Creation: Create and manage LPNs - Putaway: Location assignment and putaway - Inventory: Create inventory records during receiving - Products: View only - Locations: View, limited update (putaway) - Orders: No access - Reporting: Receiving reports only
Typical Users: - Receiving dock staff - Inbound logistics coordinators - Putaway associates
Permission Count: 40 permissions
Picker/Warehouse Associate¶
Access Level: Order fulfillment operations
Permissions: - Orders: View assigned pick lists, update pick status - Picking: Full picking workflow access - Packing: Full packing workflow access - Inventory: View only - Locations: View only - Products: View only - Shipping: View only (no shipment creation) - Receiving: No access
Typical Users: - Order pickers - Packers - Warehouse associates - Fulfillment staff
Permission Count: 30 permissions
Shipping Clerk¶
Access Level: Shipping operations
Permissions: - Shipments: Full CRUD access - Carriers: View, create shipments - Orders: View, update shipping status - Packing: View packed orders - Labels: Print shipping labels - Tracking: Update tracking information - Receiving: No access - Reporting: Shipping reports only
Typical Users: - Shipping coordinators - Outbound logistics staff - Carrier coordination staff
Permission Count: 38 permissions
Customer Service¶
Access Level: Read-only order and customer information
Permissions: - Orders: View only, no modifications - Customers: View only - Shipments: View tracking and status - Inventory: View availability only - Products: View only - Reporting: Customer and order reports - All Other Modules: No access
Typical Users: - Customer service representatives - Sales support staff - Account managers
Permission Count: 25 permissions (all read-only)
Creating Custom Roles¶
Create organization-specific roles tailored to unique workflows:
Step-by-Step Process¶
1. Access Role Creation - Click Add Role button - Create Role modal appears
2. Basic Information
Enter role details:
- Role Name: Descriptive name (e.g., "Quality Control Specialist")
- Description: Explanation of role purpose and intended users
- Role Type: Custom (system roles cannot be created)
- Active Status: Enable or disable role
3. Permission Selection
Assign permissions to the role:
- Permissions organized by module (Inventory, Orders, etc.)
- Each module shows available operations (View, Create, Edit, Delete)
- Check boxes to grant specific permissions
- Use "Select All" for full module access
- Use permission groups for common combinations
4. Permission Groups
Predefined permission bundles:
- Read Only: View-only access to all checked modules
- Standard Operations: View, Create, Edit (no Delete)
- Full Access: All CRUD operations for checked modules
- Administrative: Includes configuration and management permissions
5. Review and Save
- Review selected permissions count
- Verify permission combinations make sense
- Click Create Role
- Role immediately available for user assignment
Custom Role Examples¶
Quality Control Inspector: - Receiving: View, Create (inspection records) - Inventory: View, Update (quality holds) - Products: View only - Reporting: Quality reports
Cycle Count Specialist: - Inventory: View, Update (counts) - Cycle Counts: Full CRUD access - Locations: View only - Products: View only - Reporting: Cycle count reports
Returns Processor: - Orders: View, Update (return status) - Receiving: Create (return receipts) - Inventory: Create (restocking) - Customers: View only - Reporting: Returns reports
Permission System¶
Module Permissions¶
Permissions are organized by functional modules:
Core Operations Modules: - Dashboard - Inventory - Products - Orders - Customers
Warehouse Operations Modules: - Receiving - Shipping - LPNs (License Plate Numbers) - Locations - Staging Areas
Administrative Modules: - Users - Roles - Settings - Bulk Upload - Templates - Reports
Billing & Finance Modules: - Invoices - Billing Events - Warehouses
Operation Permissions¶
Each module supports CRUD operations:
View (Read) - View list of records - View individual record details - Access to read-only interfaces - No data modification capability
Create - Add new records - Import data (where applicable) - Initiate workflows - Requires View permission
Update (Edit) - Modify existing records - Update status and properties - Perform operational actions - Requires View permission
Delete - Remove records from system - Cancel operations - Archive data - Requires View and Update permissions
Special Permissions¶
Beyond CRUD, some modules have special permissions:
Inventory Module: - Adjust Quantities - Transfer Between Locations - Create Cycle Counts - Approve Adjustments
Orders Module: - Allocate Inventory - Release to Warehouse - Cancel Orders - Override Allocations
Receiving Module: - Approve Receipts - Create LPNs - Assign Putaway Locations - Override Expected Quantities
Reporting Module: - Export Data - Schedule Reports - Access Financial Reports - View Audit Logs
Assigning Permissions¶
Individual Permission Assignment¶
Assign permissions one at a time:
- Edit role
- Navigate to module section
- Check permission checkboxes
- Save role
Permission Dependencies:
Some permissions require others: - Create requires View - Update requires View - Delete requires View and Update - Special operations may require Create/Update
Bulk Permission Assignment¶
Assign multiple permissions efficiently:
By Module: 1. Select module name checkbox 2. All module permissions selected 3. Or use "Select All Operations" dropdown
By Permission Group: 1. Click permission group button (Read Only, Standard, Full Access) 2. Appropriate permissions auto-selected 3. Adjust individual permissions as needed
Template-Based Assignment¶
Use existing role as template:
- Find similar existing role
- Click Duplicate action
- New role created with same permissions
- Edit role name and adjust permissions
- Save customized role
Role Hierarchy¶
Hierarchical Structure¶
Roles follow a logical hierarchy for permission inheritance:
System Administrator (All Permissions)
├── Warehouse Manager (Warehouse Operations)
│ ├── Inventory Manager (Inventory Focus)
│ ├── Receiving Supervisor (Receiving Focus)
│ └── Shipping Supervisor (Shipping Focus)
├── Warehouse Associate (Basic Operations)
│ ├── Receiving Clerk (Receiving Only)
│ ├── Picker (Picking Only)
│ └── Shipping Clerk (Shipping Only)
└── Customer Service (Read-Only)
Permission Elevation¶
Users with multiple roles receive combined permissions:
- Union of Permissions: User has ALL permissions from ALL assigned roles
- Most Permissive Wins: If one role grants access, user has access
- No Permission Conflicts: Broader permissions always take precedence
Example: - User assigned: Picker + Shipping Clerk - Permissions: All Picker permissions + All Shipping Clerk permissions - Result: Can both pick orders AND create shipments
Editing Roles¶
Modifying Existing Roles¶
Update role permissions as needs change:
System Roles: - Cannot edit standard role permissions - Cannot delete system roles - Can view permission details - Must create custom role for modifications
Custom Roles: - Full edit capability - Add or remove permissions - Change role name and description - Update active status
Edit Process¶
- Click Edit on role card
- Modify role properties
- Adjust permission selections
- Click Save Changes
- Changes immediately apply to all users with role
Impact of Changes: - Users currently logged in may need to re-login - New permissions available immediately - Removed permissions revoked immediately - Audit log records all changes
Role Deactivation¶
Temporarily disable a role:
- Edit role
- Set status to "Inactive"
- Save changes
- Users retain role assignment but permissions revoked
- Reactivate later without reassigning to users
Role Assignment¶
Assigning to Users¶
Users receive roles during account creation or editing:
During User Creation: 1. Create new user 2. Select role from dropdown 3. User inherits all role permissions 4. Can assign multiple roles if needed
For Existing Users: 1. Edit user account 2. Add or remove role assignments 3. Save changes 4. User permissions update immediately
Multi-Role Assignment¶
Users can have multiple roles:
Use Cases: - Hybrid positions (e.g., Receiver who also ships) - Temporary expanded access (e.g., covering for manager) - Cross-training (e.g., picker learning receiving) - Specialized access (e.g., base role + reporting access)
Best Practices: - Limit to 2-3 roles per user - Ensure roles don't conflict in purpose - Document reason for multiple roles - Review regularly for continued necessity
Permission Inheritance¶
Inherited Permissions¶
Users inherit permissions from all assigned roles:
Single Role: - User has exactly the permissions defined in role - Straightforward permission auditing - Easy to understand access level
Multiple Roles: - User has union of all role permissions - More complex permission set - Requires careful role selection
Effective Permissions¶
View user's actual permissions:
- Navigate to user account
- View "Effective Permissions" section
- See complete list from all roles
- Permissions marked with source role
- Understand full access scope
Permission Conflicts¶
Handling conflicting permissions:
Scenario: User has Picker role (orders: view only) + Warehouse Manager role (orders: full CRUD)
Resolution: Most permissive wins - user has full CRUD on orders
Principle: Roles add permissions, never restrict
Best Practices¶
Role Design¶
- Least Privilege: Grant minimum permissions needed for job function
- Job-Based Roles: Define roles by position, not individual
- Logical Grouping: Group related permissions together
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive, unambiguous role names
- Documentation: Maintain description of role purpose
Permission Management¶
- Regular Review: Audit roles quarterly for permission accuracy
- Change Control: Document reasons for permission changes
- Testing: Test new roles with test users before production
- Incremental Grants: Start restrictive, add permissions as needed
- Emergency Access: Have process for temporary permission elevation
Security¶
- Segregation of Duties: Separate create/approve permissions
- Sensitive Operations: Require elevated roles for critical actions
- Audit Logging: Enable and review permission change logs
- Role Certification: Require periodic role access recertification
- Temporary Access: Use role activation/deactivation for temporary needs
Organizational Alignment¶
- Match Org Chart: Align roles with organizational structure
- Consistent Naming: Use company-standard position titles
- Cross-Training: Create training roles with limited permissions
- Seasonal Roles: Define roles for temporary/seasonal staff
- Contractor Roles: Separate roles for external users
Security Considerations¶
Separation of Duties¶
Implement controls to prevent fraud:
Examples: - Receiving Clerk cannot approve own receipts (needs supervisor approval) - Picker cannot also ship (requires shipping clerk verification) - Inventory adjuster cannot delete adjustment records
Implementation: - Create distinct roles for each function - Require approval workflows for sensitive operations - Monitor for users with conflicting role combinations
Privileged Access¶
Control administrative capabilities:
System Administrator: - Limit to IT staff only - Require MFA for admin accounts - Monitor admin activities closely - Separate from operational accounts
Role Managers: - Restrict who can create/modify roles - Require approval for permission changes - Audit role modifications regularly
Compliance¶
Meet regulatory requirements:
SOC 2: - Document role definitions and assignments - Maintain audit trail of permission changes - Regular access reviews
GDPR: - Control access to customer personal data - Limit data export permissions - Track data access activities
Industry-Specific: - Healthcare (HIPAA): Role-based data access controls - Finance (SOX): Separation of duties enforcement - Retail (PCI-DSS): Limit payment data access
Troubleshooting¶
User Cannot Access Feature¶
Symptom: User cannot see or use specific feature despite having apparent access
Solutions: 1. Check user's assigned role(s) 2. Review effective permissions for user 3. Verify feature requires specific permission 4. Confirm role includes required permission 5. Check if permission has dependencies 6. Verify user status is Active 7. Ask user to log out and back in
Permission Not Taking Effect¶
Symptom: Role updated but user still has old permissions
Solutions: 1. Wait a few seconds for cache refresh 2. User should log out and log back in 3. Check role edit was saved successfully 4. Verify user still assigned to role 5. Review effective permissions to confirm change 6. Check browser cache (clear if needed)
Too Many Permissions¶
Symptom: User has more access than intended
Solutions: 1. Review all assigned roles 2. Check for unintended multi-role assignment 3. Review each role's permissions 4. Remove unnecessary role assignments 5. Create more restrictive custom role if needed 6. Verify permission inheritance is understood
Cannot Edit System Role¶
Symptom: Edit button grayed out or missing for standard role
Solutions: 1. System roles cannot be edited (by design) 2. Create custom role based on system role 3. Duplicate system role and modify copy 4. Assign custom role to users instead 5. Document customizations for audit purposes
Role Deletion Blocked¶
Symptom: Cannot delete custom role
Solutions: 1. Check if users currently assigned to role 2. Reassign users to different role first 3. Deactivate role instead of deleting (preserves history) 4. System roles cannot be deleted (ever) 5. Review audit log for role usage history
Related Documentation¶
- Users - User account management and role assignment
- Settings - System-wide security settings
- Bulk Upload - Bulk user/role import
Support¶
For role management assistance:
- Email: support@zoratech.io
- FAQ: Role Management FAQ
- Troubleshooting: Common Issues